Decentralized Web Nodes
3 minute read
A Decentralized Web Node is a data storage and message relay mechanism that entities can use to locate public or private permissioned data related to a given DID.
Personal Data Store
A DWN is a personal data store. This means you can:
- Own your data: You decide where to host your node. You control who has access.
- Back up your data: Host multiple nodes in different places, keep them all synced. If one goes down, you have your back up. When it comes back up, the sync is effortless.
- Send and receive data: Alice controls her DWN using her DID. Bob controls his DWN with his DID. Alice can send data to Bob just by resolving his DID.
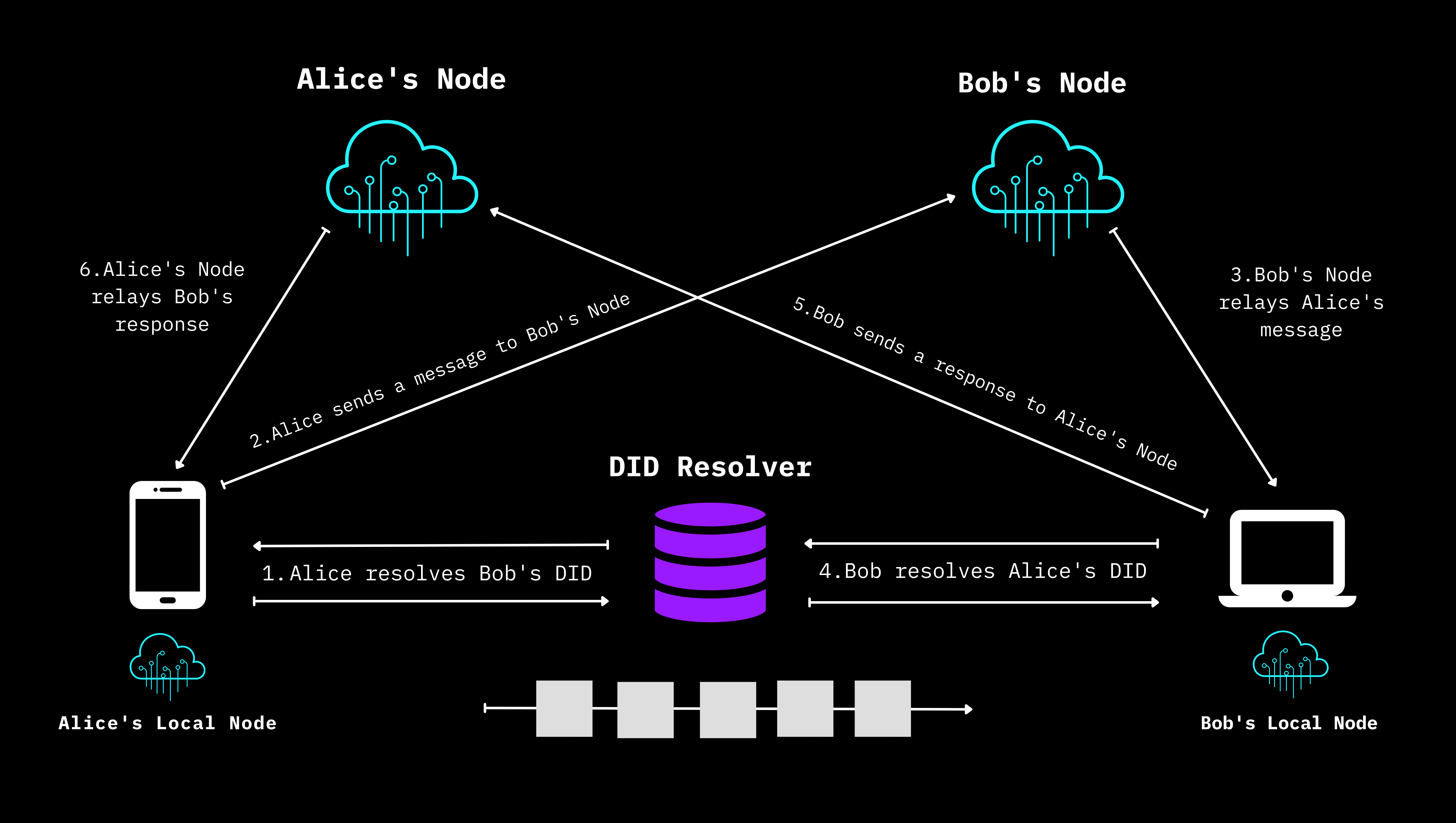
Topology of an exchange between Decentralized Web Nodes, duplicated from the DIF Decentralized Web Node Spec
Authorization
DWNs have two mechanisms to allow others access to read, write, or delete data on you node.
- Permissions: Allow someone access to read, write, or delete specific data records on your node.
- Protocols: Install a protocol that lets you define data types and authorization for a decentralized web app.
The easiest way to understand this distinction is to think of permissions as active, explicit, and manual, whereas protocols are passive, syntactic, and contractual.
Data Model
Data types are bound to known schemas, letting applications agree on data models. This opens the door to applications working together in ways that's been much more difficult in traditional development platform.
Messaging
All communication is done through simple JSON objects called messages. Web5 constructs messages and helps you send them to their destination by resolving a recipient's DID and getting the address of their Decentralized Web Node. A message can install protocols, grant permissions, and read, write, query, or delete a record. For example, a message writing a record to a DWN may look like the example below.
{ // Message
"recordId": "b65b7r8n7bewv5w6eb7r8n7t78yj7hbevsv567n8r77bv65b7e6vwvd67b6",
"descriptor": {
"parentId": CID(PREVIOUS_DESCRIPTOR),
"dataCid": CID(data),
"dateCreated": 123456789,
"published": true,
"encryption": "jwe",
"interface": "Records",
"method": "Write",
"schema": "https://schema.org/SocialMediaPosting",
"commitStrategy": "json-merge",
"dataFormat": DATA_FORMAT
}
}
See the DWN spec for a detailed explanation of each field.
Was this page helpful?
Connect with us on Discord
Submit feedback: Open a GitHub issue
Edit this page: GitHub Repo
Contribute: Contributing Guide